Pre-processing data
The purpose of pre-processing is to improve the overall quality of the data. The raw data contains information, such as foreground and background signals as well as quality statistics, about all the spots detected on an array. The
quality of the spots may vary. Information from poor quality spots
is hard to trust and should therefore be removed from the dataset. This can
be done by passing the raw data through different filters. There may also be errors associated with the data, including
systematic errors from the technical or experimental procedures. Systematic errors
can be reduced by normalising the data. Normalisation is therefore an important
step in pre-processing data.
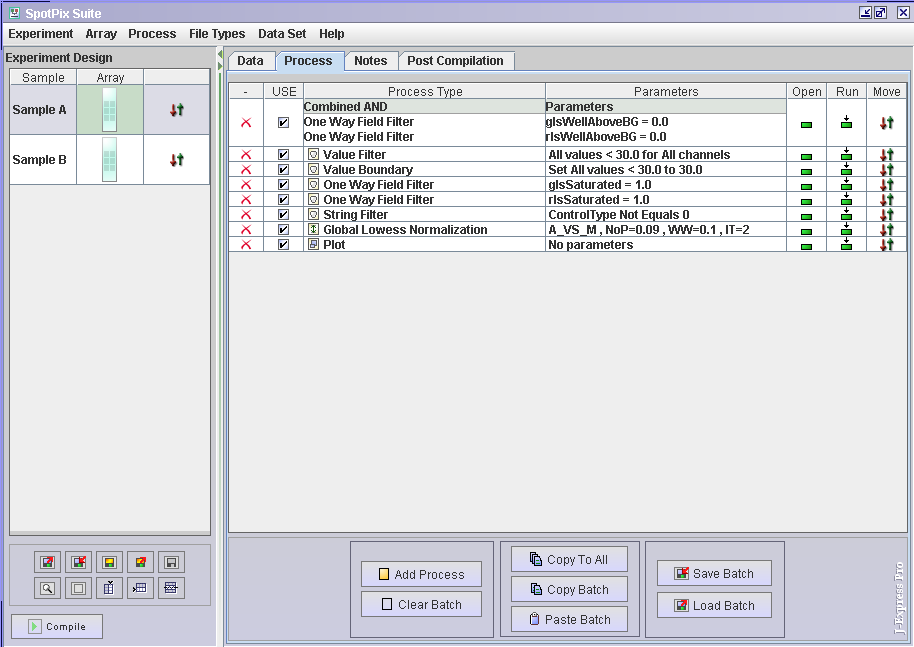
- Select an array by clicking on a

- Click the Process tab
- Filter and normalisation procedures are added by clicking on the
 button and choosing the wanted process. The raw data files decide which filters you can apply. This may vary from different formats and different array platforms. To get an idea of the possibilities, it is a good idea to make a copy of one of the data files and then open the copy in e.g. Excel. This will allow you to get familiar with the different columns available, as well as the type of values they contain. If you for instance want to remove control spots, you must find out which column contains this information and use the names for the filter. Suggestions for filtering steps for different arrayplatforms can be found here:
button and choosing the wanted process. The raw data files decide which filters you can apply. This may vary from different formats and different array platforms. To get an idea of the possibilities, it is a good idea to make a copy of one of the data files and then open the copy in e.g. Excel. This will allow you to get familiar with the different columns available, as well as the type of values they contain. If you for instance want to remove control spots, you must find out which column contains this information and use the names for the filter. Suggestions for filtering steps for different arrayplatforms can be found here:
- To see what the different filtering and normalisation methods does to the data, it is always good to have a plot
- See here how can you add a plot.
- When you have some processes in your list you can move this plot up and down the list by clicking and dragging the
 in the Move column. If you click on the plot in the Run column, the plot will show how the processes above the plot row have affected the data.
in the Move column. If you click on the plot in the Run column, the plot will show how the processes above the plot row have affected the data.
- Save the process batch when you are happy with it. This way you can load it later to make changes or use it as it is on later datasets. It saves you from having to do all the work again later.
- The processes you have added have currently only been added to the sample you selected before clicking the Process tab. Click the Copy to all button to copy the processing steps to the other arrays.
- You have now nearly finished all pre-processing. There is a User Info and Post Compilation tab.
- Use the User Info to make notes.
- Post Compilation is used to handle missing values in your dataset. You can either remove any gene that has a certain percentage of missing values, or replace the missing value. If you want to remove all genes that have at least one missing value, set the Percent Allowed Missing Values to 0. If you allow some missing values, set the percent allowed missing values, and choose the method that should be used to replace the missing values. It can sometimes be advisable to replace all missing values by 0, and make sure that Keep Missing Indices is checked. You can then replace the missing values after the compilation (from the Raw Data menu in the J-Express main window).
- When you are satisfied with the sample setup and filters press Compile.
 in the Move column. If you click on the plot in the Run column, the plot will show how the processes above the plot row have affected the data.
in the Move column. If you click on the plot in the Run column, the plot will show how the processes above the plot row have affected the data.